Childhood cancer cells drain immune system’s batteries
Cancer cells in neuroblastoma contain a molecule that breaks down a key energy source for the body’s immune cells, leaving them too physically drained to fight the disease, according to new research. Cancer Research UK-funded scientists have discovered that the cells in neuroblastoma – a rare type of childhood cancer that affects nerve cells – produce a molecule that breaks down arginine, one of the building blocks of proteins and an essential energy source for immune cells.
Crystal clear images uncover secrets of hormone receptors

Many hormones and neurotransmitters work by binding to receptors on a cell’s exterior surface. This activates receptors causing them to twist, turn and spark chemical reactions inside cells. NIH scientists used atomic level images to show how the neuropeptide hormone neurotensin might activate its receptors. Their description is the first of its kind for a neuropeptide-binding G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), a class of receptors involved in a wide range of disorders and the target of many drugs.
Paralyzed men move legs with new non-invasive spinal cord stimulation
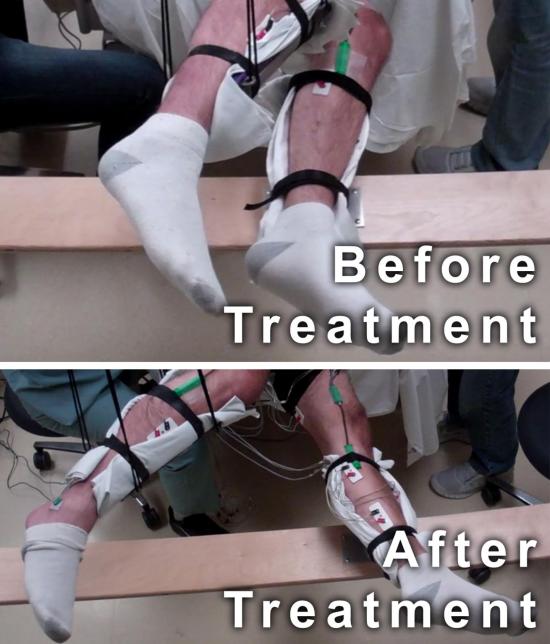
This image shows the range of voluntary movement prior to receiving stimulation compared to movement after receiving stimulation, physical conditioning, and buspirone. The subject’s legs are supported so that they can move without resistance from gravity. The electrodes on the legs are used for recording muscle activity.
Image credit goes to: Edgerton lab/UCLA
Five men with complete motor paralysis were able to voluntarily generate step-like movements thanks to a new strategy that non-invasively delivers electrical stimulation to their spinal cords. The strategy, called transcutaneous stimulation, delivers electrical current to the spinal cord by way of electrodes strategically placed on the skin of the lower back.
Where memory is encoded and retrieved
Are the same regions and even the same cells of the brain area called hippocampus involved in encoding and retrieving memories or are different areas of this structure engaged? This question has kept neuroscientists busy for a long time. Researchers at the Mercator Research Group “Structure of Memory” at RUB have now found out that the same brain cells exhibit activity in both processes.
Sleep not just protects memories against forgetting, it also makes them more accessible
Sleeping not only protects memories from being forgotten, it also makes them easier to access, according to new research from the University of Exeter and the Basque Centre for Cognition, Brain and Language. The findings suggest that after sleep we are more likely to recall facts which we could not remember while still awake.
Cell phone notifications may be driving you to distraction
Whether you are alerted to an incoming phone call or text by a trendy ringtone, an alarm bell or a quiet vibration, just receiving a notification on your cell phone can cause enough of a distraction to impair your ability to focus on a given task. In fact, the distraction caused by a simple notification — whether it is a sound or a vibration — is comparable to the effects seen when users actively use their cell phones to make calls or send text messages, the researchers found.
Brain structure reveals ability to regulate emotions
We all vary in how often we become happy, sad or angry, and also in how strongly these emotions are expressed. This variability is a part of our personality and can be seen as a positive aspect that increases diversity in society. However, there are people that find it so difficult to regulate their emotions that it has a serious impact on their work, family and social life. These individuals may be given an emotional instability diagnosis such as borderline personality disorder or antisocial personality disorder.
Static synapses on a moving structure: Mind the gap!
In biology, stability is important. From body temperature to blood pressure and sugar levels, our body ensures that these remain within reasonable limits and do not reach potentially damaging extremes. Neurons in the brain are no different and, in fact, have developed a number of ways to stabilise their electrical activity so as to avoid becoming either overexcitable, potentially leading to epilepsy, or not excitable enough, leading to non functional neurons.
What’s that!? Brain network that controls, redirects attention identified
Researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) have found that key parts of the human brain network that give us the power to control and redirect our attention–a core cognitive ability–may be unique to humans. The research suggests that the network may have evolved in response to increasingly complex social cues.
Intellectual pursuits may buffer the brain against addiction
New study of mice finds that intellectual pursuits can make us more resistant to the lure of drugs Image credit goes to: Emily Strange)
Challenging the idea that addiction is hardwired in the brain, a new study suggests that even a short time spent in a stimulating learning environment can rewire the brain’s reward system and buffer it against drug dependence. Scientists tracked cocaine cravings in more than 70 adult male mice and found that those rodents whose daily drill included exploration, learning and finding hidden tasty morsels were less likely than their enrichment-deprived counterparts to seek solace in a chamber where they had been given cocaine.
Baby’s first stool can alert doctors to future cognitive issues
A newborn’s first stool can signal the child may struggle with persistent cognitive problems, according to Case Western Reserve University Project Newborn researchers. In particular, high levels of fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEE) found in the meconium (a newborn’s first stool) from a mother’s alcohol use during pregnancy can alert doctors that a child is at risk for problems with intelligence and reasoning.
Spinal cord injury and the bodies response: Modulating the macrophage
Macrophages are cellular sentinels in the body, assigned to identify “attacks” from viruses, bacteria, or fungi and sound the alarm when they are present. However, these cells are a “double edged sword” in spinal cord injury, providing both neural repair-promoting properties and pathological functions that destroy neuronal tissue.
A new wrinkle: Geometry of brain’s outer surface correlates with genetic heritage
In the study, the researchers found that the shape of the cerebral cortex correlates with genetic ancestry. Image credit goes to: UC San Diego
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego and the School of Medicine have found that the three-dimensional shape of the cerebral cortex – the wrinkled outer layer of the brain controlling many functions of thinking and sensation – strongly correlates with ancestral background. The study opens the door to more precise studies of brain anatomy going forward and could eventually lead to more personalized medicine approaches for diagnosing and treating brain diseases.
Study shows long-term effects of type 2 diabetes on the brain, thinking
In just two years, people with type 2 diabetes experienced negative changes in their ability to regulate blood flow in the brain, which was associated with lower scores on tests of cognition skills and their ability to perform their daily activities, according to a new study.
Long-term memories are maintained by prion-like proteins

Research from Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) has uncovered further evidence of a system in the brain that persistently maintains memories for long periods of time. And paradoxically, it works in the same way as mechanisms that cause mad cow disease, kuru, and other degenerative brain diseases.
REM sleep critical for young brain development; medication interferes
Rapid eye movement or REM sleep actively converts waking experiences into lasting memories and abilities in young brains reports a new study. The finding broadens the understanding of children’s sleep needs and calls into question the increasing use of REM-disrupting medications such as stimulants and antidepressants.
Novel DNA repair mechanism brings new horizons
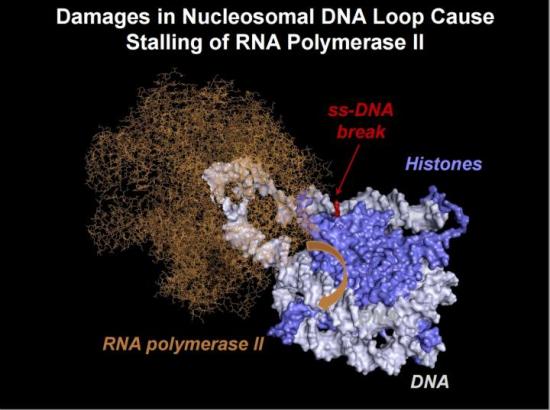
Estimated structure of the nucleosomal DNA loops, which are temporarily formed during transcription of chromatin containing intact DNA by RNA polymerase II (Pol II). In the presence of a single-strand DNA break, the loop structure likely changes, preventing rotation of the RNA polymerase along the DNA helix (orange arrow).
Image credit goes to: Nadezhda S. Gerasimova et al
The DNA molecule is chemically unstable giving rise to DNA lesions of different nature. That is why DNA damage detection, signaling and repair, collectively known as the DNA damage response, are needed. A group of researchers discovered a new mechanism of DNA repair, which opens up new perspectives for the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases.
New epigenetic mechanism revealed in brain cells
For decades, researchers in the genetics field have theorized that the protein spools around which DNA is wound, histones, remain constant in the brain, never changing after development in the womb. Now, researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have discovered that histones are steadily replaced in brain cells throughout life – a process which helps to switch genes on and off.
Omega-3 supplements and antioxidants may help with preclinical Alzheimer’s disease
Here’s more evidence that fish oil supplementation and antioxidants might be beneficial for at least some people facing Alzheimer’s disease. A new report describes the findings of a very small study in which people with mild clinical impairment, such as those in the very early stages of the disease, saw clearance of the hallmark amyloid-beta protein and reduced inflammation in neurological tissues. Although the findings involved just 12 patients over the course of 4 to 17 months, the findings suggest further clinical study of this relatively inexpensive and plentiful supplement should be conducted.
How your brain knows it’s summer

Researchers led by Toru Takumi at the RIKEN Brain Science Institute in Japan have discovered a key mechanism underlying how animals keep track of the seasons. The study shows how circadian clock machinery in the brain encodes seasonal changes in daylight duration through GABA activity along with changes in the amount of chloride located inside certain neurons.
Rare neurons enable mental flexibility

Behavioral flexibility — the ability to change strategy when the rules change — is controlled by specific neurons in the brain, Researchers have confirmed. Cholinergic interneurons are rare — they make up just one to two percent of the neurons in the striatum, a key part of the brain involved with higher-level decision-making. Scientists have suspected they play a role in changing strategies, and researchers at OIST recently confirmed this with experiments.
Brain scan can predict who responds best to certain treatment for OCD
Tens of millions of Americans — an estimated 1 to 2 percent of the population — will suffer at some point in their lifetimes from obsessive-compulsive disorder, a disorder characterized by recurrent, intrusive, and disturbing thoughts (obsessions), and/or stereotyped recurrent behaviors (compulsions). Left untreated, OCD can be profoundly distressing to the patient and can adversely affect their ability to succeed in school, hold a job or function in society.
Autism: The value of an integrated approach to diagnosis
Researchers at Inserm (Inserm Unit 930 “Imaging and Brain”) attached to François-Rabelais University and Tours Regional University Hospital have combined three clinical, neurophysiological and genetic approaches in order to better understand the brain mechanisms that cause autism. When tested on two families, this strategy enabled the researchers to identify specific gene combinations in autistic patients that distinguished them from patients with intellectual disabilities.
Liar, Liar: Children with good memories are better liars
Children who benefit from a good memory are much better at covering up lies, researchers from the University of Sheffield have discovered. Experts found a link between verbal memory and covering up lies following a study which investigated the role of working memory in verbal deception amongst children.
Musicians don’t just hear in tune, they also see in tune
Musicians don’t just hear in tune, they also see in tune. That is the conclusion of the latest scientific experiment designed to puzzle out how the brain creates an apparently seamless view of the external world based on the information it receives from the eyes.
Cell density remains constant as brain shrinks with age
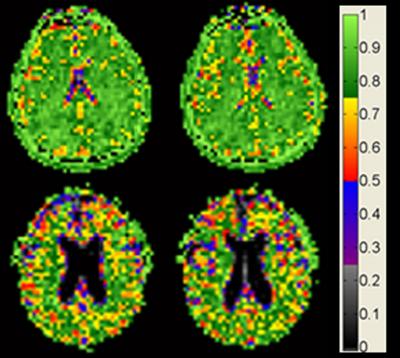
Brain cell density remains constant with age among cognitively normal adults. Image credit goes to: Dr. Keith Thulborn
New, ultra-high-field magnetic resonance images (MRI) of the brain by researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago provide the most detailed images to date to show that while the brain shrinks with age, brain cell density remains constant. The images provide the first evidence that in normal aging, cell density is preserved throughout the brain, not just in specific regions, as previous studies on human brain tissue have shown.
Largest-ever study of parental age and autism finds increased risk with teen moms
The largest-ever multinational study of parental age and autism risk, funded by Autism Speaks, found increased autism rates among the children of teen moms and among children whose parents have relatively large gaps between their ages. The study also confirmed that older parents are at higher risk of having children with autism. The analysis included more than 5.7 million children in five countries.
DNA breakage underlies both learning, age-related damage
The process that allows our brains to learn and generate new memories also leads to degeneration as we age, according to a new study. The finding could ultimately help researchers develop new approaches to preventing cognitive decline in disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease. Each time we learn something new, our brain cells break their DNA, creating damage that the neurons must immediately repair.
A patient’s budding cortex — in a dish?

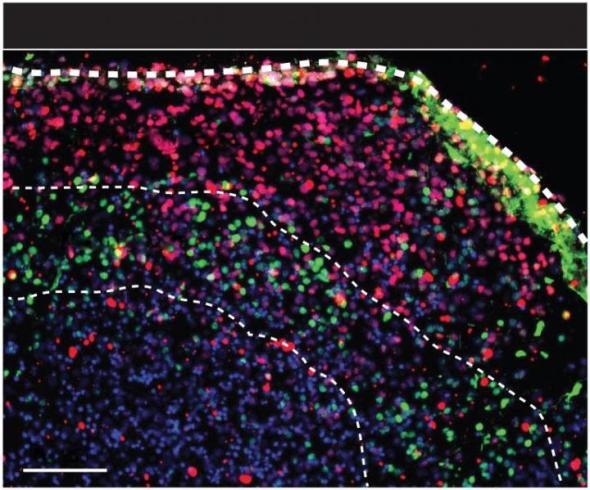
Neurons and supporting cells in the spheroids form layers and organize themselves according to the architecture of the developing human brain and network with each other.
Image credit goes to: Sergiu Pasca, M.D., Stanford University
A patient tormented by suicidal thoughts gives his psychiatrist a few strands of his hair. She derives stem cells from them to grow budding brain tissue harboring the secrets of his unique illness in a petri dish. She uses the information to genetically engineer a personalized treatment to correct his brain circuit functioning. Just Sci-fi? Yes, but…
Babies can think before they can speak
Two pennies can be considered the same — both are pennies, just as two elephants can be considered the same, as both are elephants. Despite the vast difference between pennies and elephants, we easily notice the common relation of sameness that holds for both pairs. Analogical ability — the ability to see common relations between objects, events or ideas — is a key skill that underlies human intelligence and differentiates humans from other apes.
Researchers find essential fats for brain growth
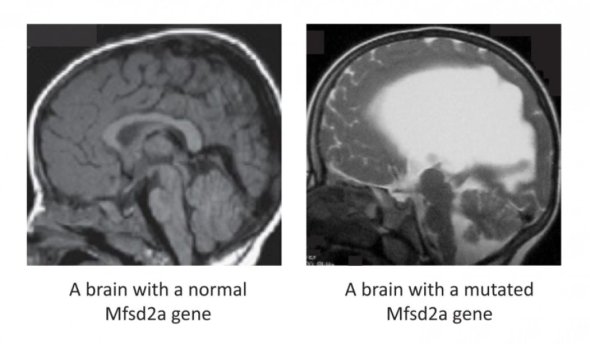
The difference between a brain with a normal Mfsd2a gene and a brain with a mutated Mfsd2a gene.
Image credit goes to: Guemez-Gamboa et al./ Nature Genetics
New research has proved that certain special fats found in blood are essential for human brain growth and function. The two studies showed that mutations in the protein Mfsd2a causes impaired brain development in humans. Mfsd2a is the transporter in the brain for a special type of fat called lysophosphatidylcholines (LPCs) — composed of essential fatty acids like omega-3. These studies show, for the first time, the crucial role of these fats in human brain growth and function.
This is your brain, on video games
A new study shows that while video game players (VGPs) exhibit more efficient visual attention abilities, they are also much more likely to use navigation strategies that rely on the brain’s reward system (the caudate nucleus) and not the brain’s spatial memory system (the hippocampus). Past research has shown that people who use caudate nucleus-dependent navigation strategies have decreased grey matter and lower functional brain activity in the hippocampus.
Omega-3 as an intervention for childhood behavioral problems
We don’t usually think of a child’s behavior as a diet issue, but if new findings hold true, then that might be the very case. In a new study, researchers suggest that omega-3, a fatty acid commonly found in fish oil, may have long-term neurodevelopmental effects that ultimately reduce antisocial and aggressive behavior problems in children.
Are infections making you stupid?
New research shows that infections can impair your cognitive ability measured on an IQ scale. The study is the largest of its kind to date, and it shows a clear correlation between infection levels and impaired cognition. Anyone can suffer from an infection, for example in their stomach, urinary tract or skin. However, a new Danish study shows that a patient’s distress does not necessarily end once the infection has been treated.
(More) bad news for Vets: PTSD linked to accelerated aging
Before PTSD had a name there was shellshock. It was mysterious and much like today, not everyone showed symptoms so — for the most part — it was written off. In recent years however, public health concerns about post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have risen significantly, driven in part by affected military veterans returning home. While this has opened the door for better care for people suffering from PTSD, it has also lead to some startling revelations about the extent of damage. New research that was just released, sad to say, doesn’t bode well for people with PTSD either.
Researchers find new clues in treating chronic pain
A chemical in the brain typically associated with cognition, movement and reward-motivation behavior — among others — may also play a role in promoting chronic pain, according to new research. The chemical, dopamine, sets the stage for many important brain functions, but the mechanisms that cause it to contribute to chronic pain are less well understood.
Mind reading: Researchers observe moment a mind is changed
Researchers studying how the brain makes decisions have, for the first time, recorded the moment-by-moment fluctuations in brain signals that occur when a monkey making free choices has a change of mind. The findings result from experiments led by electrical engineering Professor Krishna Shenoy, whose Stanford lab focuses on movement control and neural prostheses – such as artificial arms – controlled by the user’s brain.
Pesticides alter bees’ brains, making them unable to live and reproduce adequately
A new report suggests that a particular class of pesticides called “neonicotinoids” wreaks havoc on the bee populations, ultimately putting some crops that rely on pollination in jeopardy. Specifically, these pesticides kill bee brain cells, rendering them unable to learn, gather food and reproduce. The report, however, also suggests that the effects of these pesticides on bee colonies may be reversible by decreasing or eliminating the use of these pesticides on plants pollinated by bees and increasing the availability of “bee-friendly” plants available to the insects.
The adolescent brain on alcohol: Changes last into adulthood
Repeated alcohol exposure during adolescence results in long-lasting changes in the region of the brain that controls learning and memory, according to a research team at Duke Medicine that used a rodent model as a surrogate for humans. The study provides new insights at the cellular level for how alcohol exposure during adolescence, before the brain is fully developed, can result in cellular and synaptic abnormalities that have enduring, detrimental effects on behavior.
Botox makes unnerving journey into our nervous system
New research might bring a frown to even the most heavily botoxed faces, with scientists finding how some of the potent toxin used for cosmetic surgery escapes into the central nervous system. Researchers have shown how Botox – also known as Botulinum neurotoxin serotype A – is transported via our nerves back to the central nervous system.
Study links brain anatomy, academic achievement, and family income
Many years of research have shown that for students from lower-income families, standardized test scores and other measures of academic success tend to lag behind those of wealthier students. Well now a new study offers another dimension to this so-called “achievement gap”After imaging the brains of high- and low-income students, they found that the higher-income students had thicker brain cortex in areas associated with visual perception and knowledge accumulation.
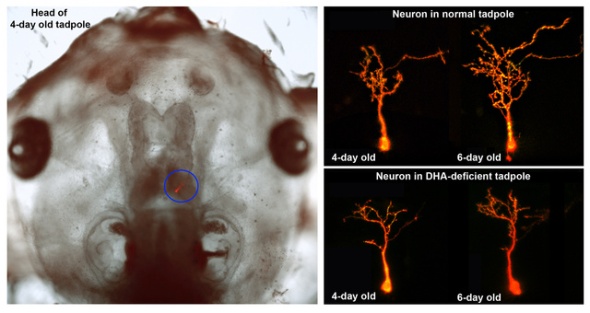
Brain development suffers from lack of fish oil fatty acids
While being inundated with advertisements directed at moms to be, skeptical parents should question the supposed health benefits of anything being sold. However, while recent reports question whether fish oil supplements support heart health, scientists have found that the fatty acids they contain are vitally important to the developing brain. Meaning there might actually be truth in advertising — this time at least.
Neuronal disorders and energy metabolism
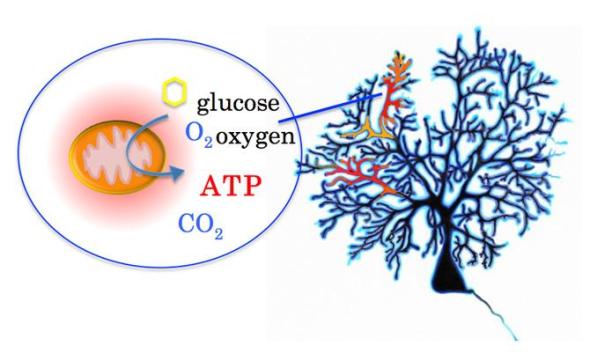
- Mitochondria are responsible for creating more than 90 percent of the energy needed by the body to sustain life and support growth. ATP energy is produced when the mitochondria transfers glucose and oxygen into water and carbon dioxide. How ATP is produced and delivered to intricate neuronal dendrites has been a mystery.
Image credit goes to: Mineko Kengaku, Kyoto University’s Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS)
Scientists in Japan have have discovered how nerve cells adjust to low energy environments during the brain’s growth process. Their study may one day help find treatments for nerve cell damage and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
Researchers find protein that triggers lupus-associated immune system activation
Researchers have identified an inflammatory molecule that appears to play an essential role in the autoimmune disorder systemic lupus erythematosus, commonly known simply as lupus. In their report the team describes finding that a protein that regulates certain cells in the innate immune system – the body’s first line of defense against infection – activates a molecular pathway known to be associated with lupus and that the protein’s activity is required for the development of lupus symptoms in a mouse model of the disease.