Study shows long-term effects of type 2 diabetes on the brain, thinking
In just two years, people with type 2 diabetes experienced negative changes in their ability to regulate blood flow in the brain, which was associated with lower scores on tests of cognition skills and their ability to perform their daily activities, according to a new study.
How the tumor escapes the immune response
Natural killer cells of the immune system can fend off malignant lymphoma cells and thus are considered a promising therapeutic approach. However, in the direct vicinity of the tumor they lose their effect. Scientists have now elucidated which mechanisms block the natural killer cells and how this blockade could be lifted.
Pupil response predicts depression risk in kids

Findings suggest that physiological reactivity to sad stimuli, assessed using pupillometry, serves as one potential biomarker of depression risk among children of depressed mothers. Image credit goes to: Jonathan Cohen, Binghamton University Photographer
Most parents don’t want to think about their children as depressed, but that can be a deadly mistake. Short of clinical diagnosis through cost prohibitive therapy, there is no real way to tell if a child is at risk for depression. However, according to new research from Binghamton University , how much a child’s pupil dilates in response to seeing an emotional image can predict his or her risk of depression over the next two years.
Link between autoimmune diseases, medications, and a dangerous heart condition

Image credit goes to: The one and only Beatrice the biologist
Mohamed Boutjdir, PhD, professor of medicine, cell biology, and physiology and pharmacology at SUNY Downstate Medical Center, has led a study with international collaborators identifying the mechanism by which patients with various autoimmune and connective tissue disorders may be at risk for life-threatening cardiac events if they take certain anti-histamine or anti-depressant medications. Dr. Boutjdir is also director of the Cardiac Research Program at VA New York Harbor Healthcare System.
Restraint and confinement still an everyday practice in mental health settings
Providers of mental-health services still rely on intervention techniques such as physical restraint and confinement to control some psychiatric hospital patients, a practice which can cause harm to both patients and care facilities, according to a new study from the University of Waterloo. The study found that almost one in four psychiatric patients in Ontario hospitals are restrained using control interventions, such as chairs that prevent rising, wrist restraints, seclusion rooms or acute control medications.
Discovery points to a new path toward a universal flu vaccine
Flu vaccines can be something of a shot in the dark. Not only must they be given yearly, there’s no guarantee the strains against which they protect will be the ones circulating once the season arrives. New research by Rockefeller University scientists suggests it may be possible to harness a previously unknown mechanism within the immune system to create more effective and efficient vaccines against this ever-mutating virus.
Long-term memories are maintained by prion-like proteins

Research from Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) has uncovered further evidence of a system in the brain that persistently maintains memories for long periods of time. And paradoxically, it works in the same way as mechanisms that cause mad cow disease, kuru, and other degenerative brain diseases.
Novel DNA repair mechanism brings new horizons
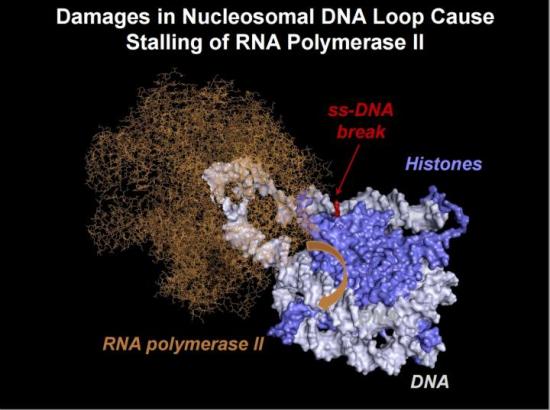
Estimated structure of the nucleosomal DNA loops, which are temporarily formed during transcription of chromatin containing intact DNA by RNA polymerase II (Pol II). In the presence of a single-strand DNA break, the loop structure likely changes, preventing rotation of the RNA polymerase along the DNA helix (orange arrow).
Image credit goes to: Nadezhda S. Gerasimova et al
The DNA molecule is chemically unstable giving rise to DNA lesions of different nature. That is why DNA damage detection, signaling and repair, collectively known as the DNA damage response, are needed. A group of researchers discovered a new mechanism of DNA repair, which opens up new perspectives for the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases.
Digesting bread and pasta can release biologically active molecules
Biologically active molecules released by digesting bread and pasta can survive digestion and potentially pass through the gut lining, suggests new research. The study reveals the molecules released when real samples of bread and pasta are digested, providing new information for research into gluten sensitivity.
New epigenetic mechanism revealed in brain cells
For decades, researchers in the genetics field have theorized that the protein spools around which DNA is wound, histones, remain constant in the brain, never changing after development in the womb. Now, researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have discovered that histones are steadily replaced in brain cells throughout life – a process which helps to switch genes on and off.
Omega-3 supplements and antioxidants may help with preclinical Alzheimer’s disease
Here’s more evidence that fish oil supplementation and antioxidants might be beneficial for at least some people facing Alzheimer’s disease. A new report describes the findings of a very small study in which people with mild clinical impairment, such as those in the very early stages of the disease, saw clearance of the hallmark amyloid-beta protein and reduced inflammation in neurological tissues. Although the findings involved just 12 patients over the course of 4 to 17 months, the findings suggest further clinical study of this relatively inexpensive and plentiful supplement should be conducted.
How your brain knows it’s summer

Researchers led by Toru Takumi at the RIKEN Brain Science Institute in Japan have discovered a key mechanism underlying how animals keep track of the seasons. The study shows how circadian clock machinery in the brain encodes seasonal changes in daylight duration through GABA activity along with changes in the amount of chloride located inside certain neurons.
Rare neurons enable mental flexibility

Behavioral flexibility — the ability to change strategy when the rules change — is controlled by specific neurons in the brain, Researchers have confirmed. Cholinergic interneurons are rare — they make up just one to two percent of the neurons in the striatum, a key part of the brain involved with higher-level decision-making. Scientists have suspected they play a role in changing strategies, and researchers at OIST recently confirmed this with experiments.
Brain scan can predict who responds best to certain treatment for OCD
Tens of millions of Americans — an estimated 1 to 2 percent of the population — will suffer at some point in their lifetimes from obsessive-compulsive disorder, a disorder characterized by recurrent, intrusive, and disturbing thoughts (obsessions), and/or stereotyped recurrent behaviors (compulsions). Left untreated, OCD can be profoundly distressing to the patient and can adversely affect their ability to succeed in school, hold a job or function in society.
A single mutation helped last year’s flu virus gain an advantage over the vaccine
The 2014-2015 flu vaccine didn’t work as well compared to previous years because the H3N2 virus recently acquired a mutation that concealed the infection from the immune system. A new study reveals the major viral mutation responsible for the mismatch between the vaccine strain and circulating strains. The research will help guide the selection of viral strains for future seasonal flu vaccines.
Synthetic biology used to engineer new route to biochemicals

Living cells can make a vast range of products for us, but they don’t always do it in the most straightforward or efficient way. Shota Atsumi, a chemistry professor at UC Davis, aims to address that through “synthetic biology:” designing and building new biochemical pathways within living cells, based on existing pathways from other living things.
Researchers find mechanisms that initiate labor
Researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have identified two proteins in a fetus’ lungs responsible for initiating the labor process, providing potential new targets for preventing preterm birth. Previous studies have suggested that signals from the fetus initiate the birth process, but the precise molecular mechanisms that lead to labor remained unclear.
Autism: The value of an integrated approach to diagnosis
Researchers at Inserm (Inserm Unit 930 “Imaging and Brain”) attached to François-Rabelais University and Tours Regional University Hospital have combined three clinical, neurophysiological and genetic approaches in order to better understand the brain mechanisms that cause autism. When tested on two families, this strategy enabled the researchers to identify specific gene combinations in autistic patients that distinguished them from patients with intellectual disabilities.
Avocados may hold the answer to beating leukemia

Professor Paul Spagnuolo from the University of Waterloo has discovered a lipid in avocados that combats acute myeloid leukemia by targeting the root of the disease — leukemia stem cells. Worldwide, there are few drug treatments available to patients that target leukemia stem cells. Image credit goes to: University of Waterloo
Rich, creamy, nutritious and now cancer fighting. New research reveals that molecules derived from avocados could be effective in treating a form of cancer. Professor Paul Spagnuolo from the University of Waterloo has discovered a lipid in avocados that combats acute myeloid leukemia (AML) by targeting the root of the disease – leukemia stem cells. Worldwide, there are few drug treatments available to patients that target leukemia stem cells.
Power of the media’s impact on medicine use revealed
More than 60,000 Australians are estimated to have reduced or discontinued their use of prescribed cholesterol-lowering statin medications following the airing of a two-part series critical of statins by ABC TV’s science program, Catalyst, a University of Sydney study reveals. The analysis of the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme medication records of 191,000 people revealed that there was an immediate impact after Catalyst was aired in October 2013, with 14,000 fewer people dispensed statins per week than expected.
Hormone that differentiates sugar, diet sweeteners could exist in humans
We’ve all been there: We eat an entire sleeve of fat-free, low-calorie cookies and we’re stuffing ourselves with more food 15 minutes later. One theory to explain this phenomenon is that artificial sweeteners don’t contain the calories or energy that evolution has trained the brain to expect from sweet-tasting foods, so they don’t fool the brain into satisfying hunger. However, until now, nobody understood how organisms distinguish between real sugar and artificial sweetener.
Cell density remains constant as brain shrinks with age
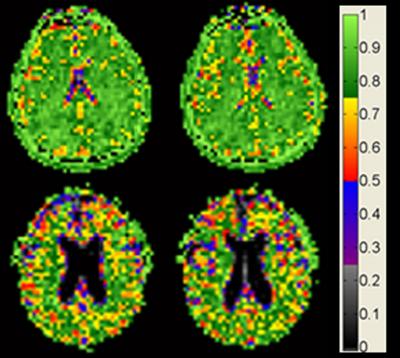
Brain cell density remains constant with age among cognitively normal adults. Image credit goes to: Dr. Keith Thulborn
New, ultra-high-field magnetic resonance images (MRI) of the brain by researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago provide the most detailed images to date to show that while the brain shrinks with age, brain cell density remains constant. The images provide the first evidence that in normal aging, cell density is preserved throughout the brain, not just in specific regions, as previous studies on human brain tissue have shown.
Autoimmunity: New immunoregulation and biomarker
Clinicians at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have elucidated a mechanism involved in determining the lifespan of antibody-producing cells, and identified a promising new biomarker for monitoring autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis and lupus erythematosus.
Milk proteins may protect against cardiovascular disease
 The Maillard reaction is a chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars that results in browned foods like seared steaks and toasted bread. When proteins and sugars are mixed together and heated, new chemical compounds are formed. Some are responsible for new flavors and some, according to a new study, may protect us against cardiovascular disease. (more…)
The Maillard reaction is a chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars that results in browned foods like seared steaks and toasted bread. When proteins and sugars are mixed together and heated, new chemical compounds are formed. Some are responsible for new flavors and some, according to a new study, may protect us against cardiovascular disease. (more…)
New drug can clear all psoriasis symptoms
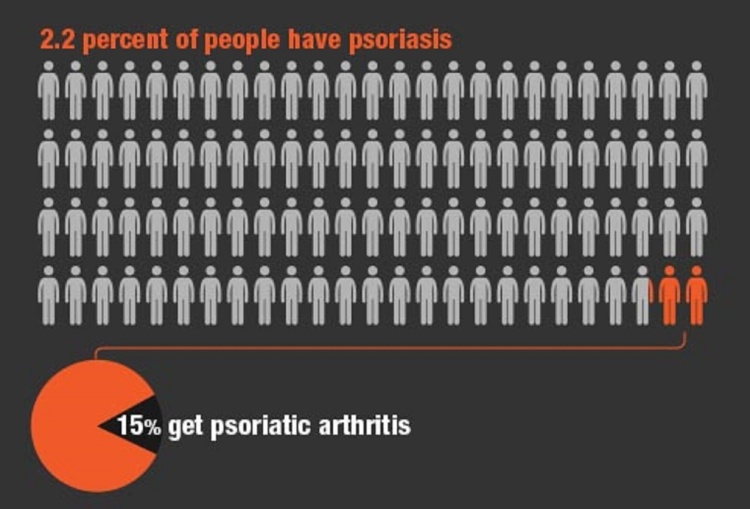
Good news for anyone who has psoriasis, a University of Manchester led trial of a new drug has resulted in 40 percent of people showing a complete clearance of psoriatic plaques after 12 weeks of treatment and over 90 percent showing improvement. The research tested 2,500 people with psoriasis. Half were given a new drug – ixekizumab – either once every two or four weeks. The other half were given a placebo or a widely used drug for psoriasis called etanercept.
First functional, synthetic immune organ with controllable antibodies created by engineers
Cornell University engineers have created a functional, synthetic immune organ that produces antibodies and can be controlled in the lab, completely separate from a living organism. The engineered organ has implications for everything from rapid production of immune therapies to new frontiers in cancer or infectious disease research.
Largest-ever study of parental age and autism finds increased risk with teen moms
The largest-ever multinational study of parental age and autism risk, funded by Autism Speaks, found increased autism rates among the children of teen moms and among children whose parents have relatively large gaps between their ages. The study also confirmed that older parents are at higher risk of having children with autism. The analysis included more than 5.7 million children in five countries.
Babies who can resettle are more likely to ‘sleep through the night’
Good news, for parents who see their babies “resettle” when they wake up. According to a video study, young infants who can “resettle” themselves after waking up are more likely to sleep for prolonged periods at night. Okay, maybe that’s bad news for parents who don’t have a baby who “resettles,” but it’s still good information.
Eating the placenta: trendy but no proven health benefits and unknown risks
Celebrities such as Kourtney Kardashian blogged and raved about the benefits of their personal placenta ‘vitamins’ and spiked women’s interest in the practice of consuming their placentas after childbirth.
How does human behavior lead to surgical errors? Researchers count the ways
Why are major surgical errors called “never events?” Because they shouldn’t happen — but do. Mayo Clinic researchers identified 69 never events among 1.5 million invasive procedures performed over five years and detailed why each occurred. Using a system created to investigate military plane crashes, they coded the human behaviors involved to identify any environmental, organizational, job and individual characteristics that led to the never events.
A patient’s budding cortex — in a dish?

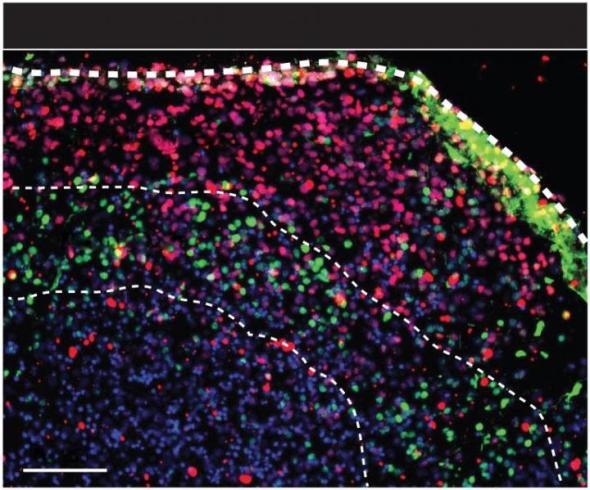
Neurons and supporting cells in the spheroids form layers and organize themselves according to the architecture of the developing human brain and network with each other.
Image credit goes to: Sergiu Pasca, M.D., Stanford University
A patient tormented by suicidal thoughts gives his psychiatrist a few strands of his hair. She derives stem cells from them to grow budding brain tissue harboring the secrets of his unique illness in a petri dish. She uses the information to genetically engineer a personalized treatment to correct his brain circuit functioning. Just Sci-fi? Yes, but…
Expanding the code of life with new ‘letters’
The DNA encoding all life on Earth is made of four building blocks called nucleotides, commonly known as “letters,” that line up in pairs and twist into a double helix. Now, two groups of scientists are reporting for the first time that two new nucleotides can do the same thing — raising the possibility that entirely new proteins could be created for medical uses.
Omega-3 as an intervention for childhood behavioral problems
We don’t usually think of a child’s behavior as a diet issue, but if new findings hold true, then that might be the very case. In a new study, researchers suggest that omega-3, a fatty acid commonly found in fish oil, may have long-term neurodevelopmental effects that ultimately reduce antisocial and aggressive behavior problems in children.
Air pollution is causing your baby problems, but breastfeeding can help
Aitana Lertxundi has conducted her research work within the framework of the INma (Childhood and Environment) programme led by Jesús Ibarluzea of the Department of Health of the Government of the Basque Autonomous Community (region). The aim is to assess how exposure to environmental pollution during pregnancy affects health and also to examine the role of diet in physical and neurobehavioural development in infancy. The study focusses on the repercussions on motor and mental development during the first years of life caused by exposure to the PM2.5 and NO2 atmospheric pollutants.
Are infections making you stupid?
New research shows that infections can impair your cognitive ability measured on an IQ scale. The study is the largest of its kind to date, and it shows a clear correlation between infection levels and impaired cognition. Anyone can suffer from an infection, for example in their stomach, urinary tract or skin. However, a new Danish study shows that a patient’s distress does not necessarily end once the infection has been treated.
Educating the immune system: A vaccine for allergies
With the arrival of spring, millions of people have begun their annual ritual of sneezing and wheezing due to seasonal allergies. However, a Canadian research team is bringing them hope with a potential vaccine that nudges the immune response away from developing allergies. The findings have major clinical implications since allergies and asthma are lifelong conditions that often start in childhood and for which there is presently no cure.
Can drinking alcohol harm the child before the mother knows she is pregnant?

Photo credit goes to: Cute moments photography
These days pregnant “moms to be” have lots of things to worry about, from second hand smoke to the chemicals in their make-up. Well they can unfortunately add one more thing to that list, a new study finds that alcohol drunk by a mouse in early pregnancy changes the way genes function in the brains of the offspring. The early exposure was also later apparent in the brain structure of the adult offspring. The timing of the exposure corresponds to the human gestational weeks 3-6 in terms of fetal development.
Researchers find new clues in treating chronic pain
A chemical in the brain typically associated with cognition, movement and reward-motivation behavior — among others — may also play a role in promoting chronic pain, according to new research. The chemical, dopamine, sets the stage for many important brain functions, but the mechanisms that cause it to contribute to chronic pain are less well understood.
Mind reading: Researchers observe moment a mind is changed
Researchers studying how the brain makes decisions have, for the first time, recorded the moment-by-moment fluctuations in brain signals that occur when a monkey making free choices has a change of mind. The findings result from experiments led by electrical engineering Professor Krishna Shenoy, whose Stanford lab focuses on movement control and neural prostheses – such as artificial arms – controlled by the user’s brain.
Walking an extra two minutes each hour may offset hazards of sitting too long
Eat less, workout more, these are the messages we are being sent almost on a daily basis. But how do we quantify “more” and who really should listen to that advice? Well a new study suggests that engaging in low intensity activities such as standing may not be enough to offset the health hazards of sitting for long periods of time. On the bright side, adding two minutes of walking each hour to your routine just might do the trick.
US clinics avoiding government oversight of ‘stem cell’ treatments
Clinics across the United States are advertising stem cell treatments that attempt to take advantage of what they perceive as exceptions in FDA regulations.The therapies in question are adipose-derived autologous stem cell treatments, in which fat cells are removed from a patient, broken down to separate components that purportedly contain stem cells, and are then reinjected into the same patient.
Scientists create worlds first genetically modified human embryos
A funny thing happened on the way to the publisher. In a world first, China has successfully created genetically modified human embryos. It was certainly an amazing piece of science, but the paper was rejected by both Nature and Science. Not because the study was flawed, or because the data was falsified, the paper was rejected for ethical reasons.
Whooping cough: A small drop in vaccine protection can lead to a case upsurge
In 2012 the USA saw the highest number of pertussis (whooping cough) cases since 1955. New research finds that a likely explanation for this rise in disease is a drop in the degree of vaccine protection for each vaccinated individual. The team worked with 60 years of pertussis disease data to determine what best explained the recent increase in the disease.
Researchers find genetic link between overactive and underactive immune systems
In the largest genetic study to date of a challenging immunodeficiency disorder, scientists have identified a gene that may be a “missing link” between overactive and underactive immune activity. The gene candidate also plays a key role in autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and even allergies.
Type 1 diabetes: On the way to an insulin vaccine
Pseudoscience claims about vaccines are seemingly hitting a fever pitch. Despite that, a new vaccine may be on the horizon for children at risk for diabetes, and that is a good thing. Researchers have found that children at risk for type 1 diabetes, who were given daily doses of oral insulin, developed a protective immune response to the disease that could lay the groundwork for a vaccine against the chronic illness.
Botox makes unnerving journey into our nervous system
New research might bring a frown to even the most heavily botoxed faces, with scientists finding how some of the potent toxin used for cosmetic surgery escapes into the central nervous system. Researchers have shown how Botox – also known as Botulinum neurotoxin serotype A – is transported via our nerves back to the central nervous system.
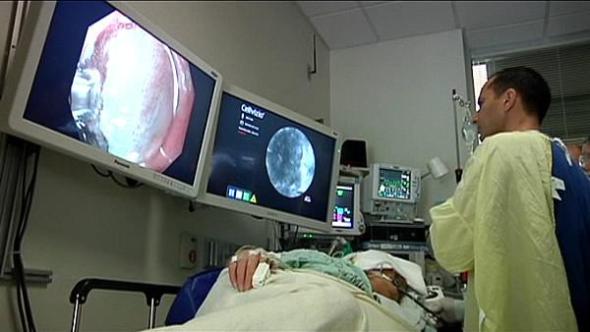
Artificial blood vessel lets researchers assess clot removal devices
For the first time, researchers have created an in vitro, live-cell artificial vessel that can be used to study both the application and effects of devices used to extract life-threatening blood clots in the brain. The artificial vessel could have significant implications for future development of endovascular technologies, including reducing the need for animal models to test new devices or approaches.
Could maple syrup help cut use of antibiotics?
Another reason to have those waffles… well maybe. Researchers have found that a concentrated extract of maple syrup makes disease-causing bacteria more susceptible to antibiotics. In an ever increasing antibiotic resistant world, this news is almost as sweet as the syrup (okay no more bad puns). The findings suggest that combining maple syrup extract with common antibiotics could increase the microbes’ susceptibility, leading to lower antibiotic usage.
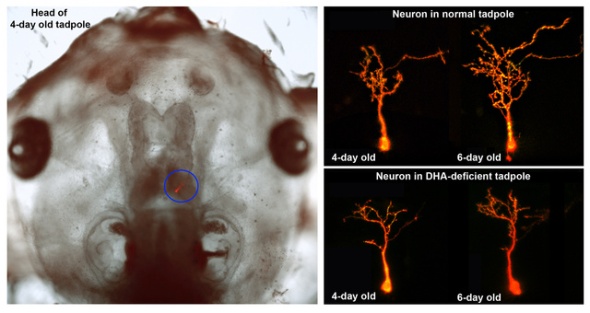
Brain development suffers from lack of fish oil fatty acids
While being inundated with advertisements directed at moms to be, skeptical parents should question the supposed health benefits of anything being sold. However, while recent reports question whether fish oil supplements support heart health, scientists have found that the fatty acids they contain are vitally important to the developing brain. Meaning there might actually be truth in advertising — this time at least.