How depression and antidepressant drugs work

Treating depression is kind of a guessing game. Trying to find a medication that works without causing side effects can take months, or more likely, years. However, new research demonstrates the effectiveness of ketamine to treat depression in a mouse model of the disease and brings together two hypotheses for the cause of depression.
Brain cells that aid appetite control identified

It’s rare for scientists to get what they describe as “clean” results without spending a lot of time repeating the same experiment over and over again. But when researchers saw the mice they were working with doubling their weight within a month or two, they knew they were on to something.
Neuroscientists discover new learning rule for pattern completion

Recently, scientists discovered a new learning rule for a specific type of excitatory synaptic connection in the hippocampus. These synapses are located in the so-called CA3 region of the hippocampus, which plays a critical role for storage and recall of spatial information in the brain. One of its hallmark properties is that memory recall can even be triggered by incomplete cues. This enables the network to complete neuronal activity patterns, a phenomenon termed pattern completion.
Could flies help us understand brain injuries?

Each year, an estimated 1.7 million people in the United States sustain traumatic brain injuries (TBIs), according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. These injuries occur most frequently from falling, but can also result from military combat, car accidents, contact sports or domestic abuse. Recently, physicians and researchers have become increasingly concerned that even mild cases of repetitive brain trauma could have long-term, unanticipated consequences.
Research shows body image linked to overall life satisfaction

We’re constantly bombarded by advertisements telling us we are too fat, too thin, not curvy enough, not flat enough — or more often than not — simply not enough. It shouldn’t be a surprise to see that effect our day to day life, like it or not — and it has. Researchers have just published results from a national study on the factors linked to satisfaction with appearance and weight.
Epigenetic study of lactose intolerance may shed light on the origin of mental illness

A new study on the epigenetics of lactose intolerance may provide an approach to understanding schizophrenia and other complex, serious illnesses. While that may seem odd, both lactose intolerance and schizophrenia are inherited. In addition, neither condition emerges in the first years of life, but rather both appear years or even decades later.
Digital media may be changing how you think

Tablet and laptop users beware. Using digital platforms such as tablets and laptops for reading may make you more inclined to focus on concrete details rather than interpreting information more abstractly, according to a new study. The findings serve as another wake-up call to how digital media may be affecting our likelihood of using abstract thought.
Smartphones uncover how the world sleeps


A pioneering study of worldwide sleep patterns combines math modeling, mobile apps and big data to parse the roles society and biology each play in setting sleep schedules. The study used a free smartphone app that reduces jetlag to gather robust sleep data from thousands of people in 100 nations. The researchers examined how age, gender, amount of light and home country affect the amount of shut-eye people around the globe get, when they go to bed, and when they wake up.
Origin of synaptic pruning process linked to learning, autism and schizophrenia identified

Vaccines don’t cause autism, but because the brain is so complex, we still don’t know how much of it works so figuring out the real causes (as in more than one) of autism has been slow going. Well, researchers have identified a brain receptor that appears to initiate adolescent synaptic pruning, a process believed necessary for learning, but in this case it is one that appears to go awry in both autism and schizophrenia.
Measuring happiness on social media

Happiness. It’s something we all strive for, but how do we measure it — as a country? A global community? Not so surprisingly, researchers are turning to social media to answer these questions and more. In a newly published study, computer scientists used two years of Twitter data to measure users’ life satisfaction, a component of happiness.
What scientists know — and don’t know — about sexual orientation

Over the last 50 years, political rights for lesbian, gay, and bisexual (LGB) individuals have significantly broadened in some countries, while they have narrowed in others. In many parts of the world, political and popular support for LGB rights hinges on questions about the prevalence, causes, and consequences of non-heterosexual orientations.
Bad news, fructose alters hundreds of brain genes

Got a sweet tooth? Maybe you even have some sugary goodness with you right now… as you are reading this. Well you may want to put that down.We know a range of diseases — from diabetes to cardiovascular disease, and from Alzheimer’s disease to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder — are linked to changes to genes in the brain. Unfortunately for those who love their pop tarts, a new study has found that hundreds of those genes can be damaged by fructose, a sugar that’s common in the Western diet, in a way that could lead to those diseases.
Are humans the new supercomputer?

As a society we have become incredibly reliant on technology, from spell check to GPS, we are slowly being replaced by computers. Need more proof, a computer can routinely beat us at chess, an AI wrote portions of a book that went on to almost win a writing contest, and if you want scary robotics enter Boston dynamics spot. So the question is, have we outlived our place in the world? Not quite. Welcome to the front line of research in cognitive skills, quantum computers and gaming.
The scientific brain: How the brain repurposes itself to learn scientific concepts

The human brain was initially used for basic survival tasks, such as staying safe and hunting and gathering. Yet, 200,000 years later, the same human brain is able to learn abstract concepts, like momentum, energy, and gravity, which have only been formally defined in the last few centuries. New research has now uncovered how the brain is able to acquire brand new types of ideas.
Could a popular painkiller hamper our ability to notice erors?

Pain, it’s a pain, it always seems to find ways to pop up when you least expect it, enter non-aspirin! Better known as acetaminophen, it has been known for centuries that is an effective painkiller. Since it is over the counter most people don’t give it a second thought, but according to a new study, it could also be impeding error-detection in the brain.
Your brain has an altered response to desirable foods

Hungry? Well, let’s face it, that pizza looks much better than the salad. Don’t deny it salad lovers, we all know behind closed doors you look at plenty of food porn to satiate your desires. Understanding the motivations that drive us to eat is important when we talk about weight loss and how we attempt to structure diets. Now a new study shows that for overweight individuals, the brain responses differently to desirable foods., but hold that thought, because there is hope.
Limitless: How long-term memories are erased and how to stop it

Currently, neuroscientists think our brain has about enough storage space to hold the entire internet. That’s a lot of space, about a petabyte in fact — if we are to believe this estimate. So, what did you read in the news this day 5 years ago? Don’t worry, I don’t even remember what I had for breakfast this morning and my long-term memory doesn’t fair much better. However, vital information about how the brain erases long-term memories has been uncovered by researchers.
What is a good death?

Food for the worms, a dirt nap, kicking the bucket, maybe there are so many euphemisms for death because it is still a taboo in certain cultures. Not so fun fact, my Uncle committed suicide some years back. I’m not going to go into details, but because suicide is looked down on, was his death still considered a “good death”? Trying to qualitatively and quantitatively define a good death, researchers have published a new paper offering help in defining the idea of a good death and have ultimately identified 11 core themes associated with dying well.
Mental illness, that’s a funny term isn’t it?


If you suffer from depression, PTSD, or anything else please visit: Take this
In today’s lexicon, the term mental illness is used pretty widely. It can be used to describe someone suffering from depression, to PTSD, to even someone suicidal. In fact, today it is sort of a catch all term for anyone who is involved in a mass shooting here in the US. We are getting off point however, why are we (myself included) labeled as mentally ill? You don’t call an amputee someone suffering from body illness, nor would you call someone with cancer “cellularly ill”.
Ancient viruses lurk in our DNA

Think your DNA is all human? Think again. And a new discovery suggests it’s even less human than scientists previously thought. Nineteen new pieces of non-human DNA — left by viruses that first infected our ancestors hundreds of thousands of years ago — have just been found, lurking between our own genes.
Forgetting, to learn

They say that once you’ve learned to ride a bicycle, you never forget how to do it. Unfortunately for students who hope this applies to studying, they might not like new research suggesting that while learning, the brain is actively trying to forget. While this may at first blush seem like a bad thing, it actually may be useful for those suffering from PTSD.
Where aging memories get stored in the brain

Think back to when you were a child. Now instead, try to think of something that happened just a few minutes ago; would you believe that you are using different portions of the brain? When we remember events which occurred recently, the hippocampus is activated. This area in the temporal lobe of the brain is a hub for learning and memory. But what happens, if we try to remember things that took place years or decades ago?
Decrypting a collagen’s role in schizophrenia

What would be worse than having bad joints? How about schizophrenia and bad joints? To be fair that isn’t what is suggested, but they may, in fact, be linked. A small peptide generated from a collagen protein may protect the brain from schizophrenia by promoting the formation of neuronal synapses and study may lead to new approaches to treating the mental disorder.
People with anxiety show fundamental differences in perception


People suffering from anxiety perceive the world in a fundamentally different way than others, according to a new study. The research may help explain why certain people are more prone to anxiety. The study shows that people diagnosed with anxiety are less able to distinguish between a neutral, “safe” stimulus (in this case, the sound of a tone) and one that had earlier been associated with gaining or losing money.
Alzheimer’s on and now Alzheimer’s off?

Alzheimer’s disease, is anything more frustrating than seeing someone — who otherwise looks healthy — start to forget who you are? Worse than that, we don’t know exactly what causes Alzheimer’s disease, or how to stop it. Well actually that might be changing. Don’t get too excited, because we’ve had false starts before, but an international group of scientists have succeeded in sorting out the mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease development and possibly distinguished its key trigger.
Want a younger brain? Stay in school — and take the stairs

Taking the stairs is normally associated with keeping your body strong and healthy. But new research shows that it improves your brain’s health too — and that education also has a positive effect. Researchers found that the more flights of stairs a person climbs, and the more years of school a person completes, the “younger” their brain physically appears.
Brain connectivity reveals your hidden motivations

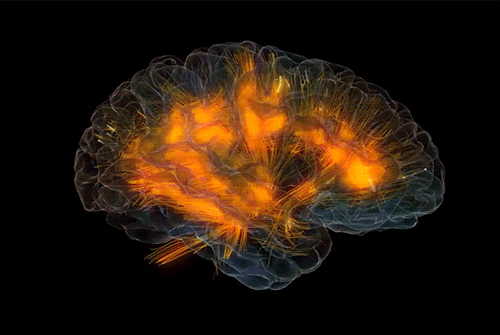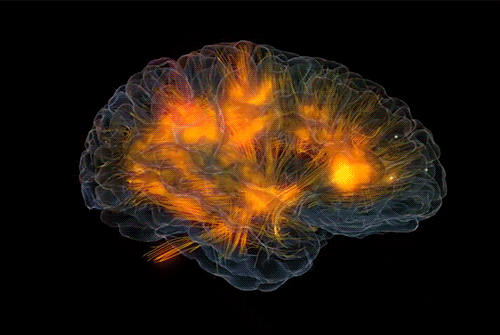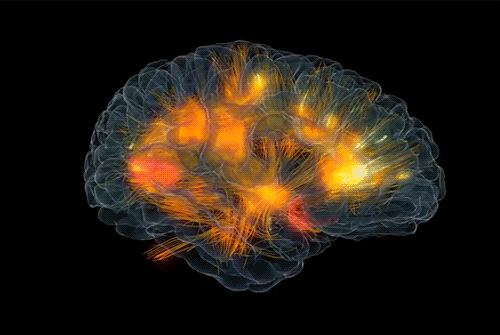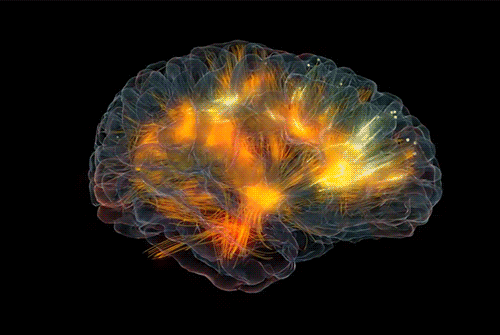
Animation from Glass Brain
To understand human behaviors, it is crucial to understand the motives behind them. So far, there was no direct way to identify motives. Simply observing behavior or eliciting explanations from individuals for their actions will not give reliable results as motives are considered to be private and people can be unwilling to unveil – or even be unaware of – their own motives.
Brain connectivity disruptions may explain cognitive deficits in people with brain injury

Cognitive impairment following a traumatic brain injury (TBI) is common, often adversely affecting quality of life for those 1.7 million Americans who experience a TBI each year. Researchers have identified complex brain connectivity patterns in individuals with chronic phases of traumatic brain injury which may explain long term higher order cognitive function deficits.
Matrix Unloaded: How you can fly a plane using expert-pilot brainwave patterns

“I know kung fu,” movie buffs might remember the remember the quote from “The Matrix.” We can all probably agree that being able to download knowledge “on tap” would be a boon to humanity. It is a shame it is just a movie… right? While that may be the case, it is just for now. That is because researchers have discovered that low-current electrical brain stimulation can modulate the learning of complex real-world skills.
Does rape alter the female brain?


Maybe we should shame rapists instead of victims?
Image credit goes to: Project Unbreakable
Sexual assault, personally, I hate the phrase. It sounds much more tame than rape and I think we should call it like it is, rape. Sure that might make a person’s skin crawl just slightly — and that is frankly the point. Rape is ugly, it’s evil, it leaves an indelible mark on a person and unfortunately a new study shows that it may be worse. Researchers have discovered that prepubescent female rodents paired with sexually experienced males had elevated levels of stress hormones, could not learn as well, and expressed reduced maternal behaviors needed to care for offspring.
The potential pathway between insomnia and depression

Have you ever had to deal with bouts of insomnia make you feel depressed? Well the good news is you’re not alone, in fact the two may be linked. A new study of firefighters suggests that insomnia and nightmares may increase the risk of depression by impairing the ability to access and leverage emotion regulation strategies effectively.
‘Jaws’ may help humans grow new teeth, shark study suggests

A new insight into how sharks regenerate their teeth, which may pave the way for the development of therapies to help humans with tooth loss, has been discovered by scientists. The study has identified a network of genes that enables sharks to develop and regenerate their teeth throughout their lifetime. The genes also allow sharks to replace rows of their teeth using a conveyer belt-like system.
All the lonely people: Pinpointing loneliness in the brain

Humans, like all social animals, have a fundamental need for contact with others. This deeply ingrained instinct helps us to survive; it’s much easier to find food, shelter, and other necessities with a group than alone. Deprived of human contact, most people become lonely and emotionally distressed.
Starting age of marijuana use may have long-term effects on brain development

The age at which an adolescent begins using marijuana may affect typical brain development, according to researchers at the Center for BrainHealth at The University of Texas at Dallas. In a paper recently published, scientists describe how marijuana use, and the age at which use is initiated, may adversely alter brain structures that underlie higher order thinking.
The molecular link between psychiatric disorders and type 2 diabetes

There may be a genetic connection between some mental health disorders and type 2 diabetes. In a new report, scientists show that a gene called “DISC1,” which is believed to play a role in mental health disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and some forms of depression, influences the function of pancreatic beta cells which produce insulin to maintain normal blood glucose levels.
Brain plasticity assorted into functional networks

Plasticity of the brain, what does that even mean? Well the good news is that it isn’t just a marketing ploy, the brain needs to be “plastic” because we need to be able to adapt. Frankly speaking, the brain still has a lot to learn about itself. Scientists at the Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute have made a key finding of the striking differences in how the brain’s cells can change through experience.
Taser shock disrupts brain function, has implications for police interrogations

More than two million citizens have been Tased by police as Taser stun guns have become one of the preferred less-lethal weapons by police departments across the United States during the past decade. But what does that 50,000-volt shock do to a person’s brain?
Investigating potential fetal exposure to antidepressants

Depression is a serious issue for expecting mothers. Left untreated, depression could have implications for a fetus’s health. But treating the disease during pregnancy may carry health risks for the developing fetus, which makes an expecting mother’s decision whether to take medication a very difficult one. To better understand how antidepressants affect fetuses during pregnancy, scientists studied exposure in mice.
Blood pressure medicine may improve conversational skills of individuals with autism

An estimated 1 in 68 children in the United States has autism. The neurodevelopmental disorder, which impairs communication and social interaction skills, can be treated with medications and behavioral therapies, though there is no cure. Now, University of Missouri researchers have found that a medication commonly used to treat high blood pressure and irregular heartbeats may have the potential to improve some social functions of individuals with autism.
The brains of patients with schizophrenia vary depending on the type of schizophrenia
I have a friend who lost an eye to his brother. Yes, you read that correctly, his brother tried to kill him and in the process he lost his eye. I’ve told this story before, but whenever new schizophrenia research comes out I feel the need to tell it again. While he has forgiven his brother (partly because not long after, he was diagnosed as schizophrenic), he will not be able to see him again until he is released from prison. A tragedy that could’ve been avoided had he been diagnosed sooner. Sadly now that he is treated, most days, you wouldn’t know he’s schizophrenic.
The music of the mind: throwing light on human consciousness

UNSW Australia scientists have shown that complex human brain activity is governed by the same simple universal rule of nature that can explain other phenomena such as the beautiful sound of a finely crafted violin or the spots on a leopard. The UNSW team has identified a link between the distinctive patterns of brain function that occur at rest and the physical structure of people’s brains.
Anxious? Chronic stress and anxiety can damage the brain

A scientific review paper warns that people need to find ways to reduce chronic stress and anxiety in their lives or they may be at increased risk for developing depression and even dementia. Led by the Rotman Research Institute at Baycrest Health Sciences, the review examined brain areas impacted by chronic anxiety, fear and stress in animal and human studies that are already published.
Overwhelmed and depressed? Well, there may be a connection

Ever feel overwhelmed when you are depressed, well the good news is it isn’t just you, the bad news is it’s probably your brain. Regions of the brain that normally work together to process emotion become decoupled in people who experience multiple episodes of depression, neuroscientists report. The findings may help identify which patients will benefit from long term antidepressant treatment to prevent the recurrence of depressive episodes.
Can you trust your gut when public speaking?

There is good news for frequent public speakers. New research shows that individuals have the ability to quickly and accurately identify a crowd’s general emotion as focused or distracted, suggesting that we can trust our first impression of a crowd’s mood.