Mexico City’s air pollution has detrimental impact on Alzheimer’s disease gene
A new study by researchers heightens concerns over the detrimental impact of air pollution on hippocampal metabolites as early markers of neurodegeneration in young urbanites carrying an allele 4 of the apolipoprotein E gene (APOE). This is associated with the risk for Alzheimer disease (AD) and a susceptibility marker for poor outcome in traumatic brain injury (TBI) recovery.
What motivates ‘Facebook stalking’ after a romantic breakup?
Social networking makes it easy to monitor the status and activities of a former romantic partner, an often unhealthy use of social media known as interpersonal electronic surveillance (IES) or, more commonly, “Facebook stalking.” Psychological and relationship factors and how individuals cope with the termination of a romantic relationship can help predict their use of online surveillance, according to a new study.
Genetic analysis supports prediction that spontaneous rare mutations cause half of autism
A team led by researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) has published a new analysis of data on the genetics of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). One commonly held theory is that autism results from the chance combinations of commonly occurring gene mutations, which are otherwise harmless. But the authors’ work provides support for a different theory.
A barrier against brain stem cell aging
Neural stem cells generate new neurons throughout life in the mammalian brain. However, with advancing age the potential for regeneration in the brain dramatically declines. Scientists now identified a novel mechanism of how neural stem cells stay relatively free of aging-induced damage. A diffusion barrier regulates the sorting of damaged proteins during cell division.
Schizophrenia: Repairing the brain
Research led by scientists from Duke-NUS Graduate Medical School Singapore (Duke-NUS) has linked the abnormal behaviour of two genes (BDNF and DTNBP1) to the underlying cause of schizophrenia. These findings have provided a new target for schizophrenia treatment.
Types of athletic training affect how brain communicates with muscles
Using endurance training or strength and resistance training not only prepares an athlete for different types of sports, they can also change the way the brain and muscles communicate with each other.
Vaccine clears some precancerous cervical lesions in clinical trial
Scientists have used a genetically engineered vaccine to successfully eradicate high-grade precancerous cervical lesions in nearly one-half of women who received the vaccine in a clinical trial. The goal, say the scientists, was to find nonsurgical ways to treat precancerous lesions caused by HPV.
Immune system may be pathway between nature and good health
Research has found evidence that spending time in nature provides protections against a startling range of diseases, including depression, diabetes, obesity, ADHD, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and many more. How this exposure to green space leads to better health has remained a mystery. After reviewing hundreds of studies examining nature’s effects on health, researchers believe the answer lies in nature’s ability to enhance the functioning of the body’s immune system.
Viruses flourish in guts of healthy babies
Bacteria aren’t the only nonhuman invaders to colonize the gut shortly after a baby’s birth. Viruses also set up house there, according to new research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. All together, these invisible residents are thought to play important roles in human health.
Diet beverage drinkers compensate by eating unhealthy food

Alcoholic drinks and sugar-sweetened beverages are associated with higher overall daily intakes, although people who drink diet beverages consume a greater percentage of non-nutritious food.
Image credit goes to: Julie McMahon
Want fries with that diet soda? You aren’t alone, and you may not be “saving” as many calories as you think by consuming diet drinks. A new study that examined the dietary habits of more than 22,000 U.S. adults found that diet-beverage consumers may compensate for the absence of calories in their drinks by noshing on extra food that is loaded with sugar, sodium, fat and cholesterol.
Female mice sing for sex

Using a sophisticated array of microphones and a sound chamber he developed, a University of Delaware researcher discovered the world is full of tiny furry Beyoncés. Studying all the Single Ladies’ communication provides insight into brain mechanics.
Image credit goes to: Jeff Chase, University of Delaware
They don’t use gondolas or croon like Sinatra. But scientists have known for a long time that male mice belt out something like love songs to females when the time seems right to them. What they didn’t know – until a University of Delaware researcher developed a sophisticated array of microphones and a sound analysis chamber – was that female mice were singing back.
Smart cells teach neurons damaged by Parkinson’s to heal themselves
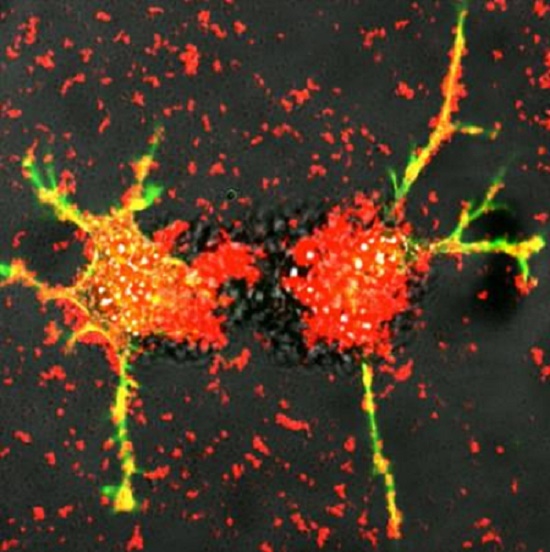
These are white blood cells reengineered by scientists at UNC-Chapel Hill deliver exosomes (red) loaded proteins that stimulate the growth of damaged nerve fibers (green and yellow). Researchers at the UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy this technique can be developing into a potential treatment for Parkinson’s disease.
Image credit goes to: Elena Batrakova/UNC Eshelman School Of Pharmacy
As a potential treatment for Parkinson’s disease, scientists at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill have created smarter immune cells that produce and deliver a healing protein to the brain while also teaching neurons to begin making the protein for themselves.
An antibody that can attack HIV in new ways
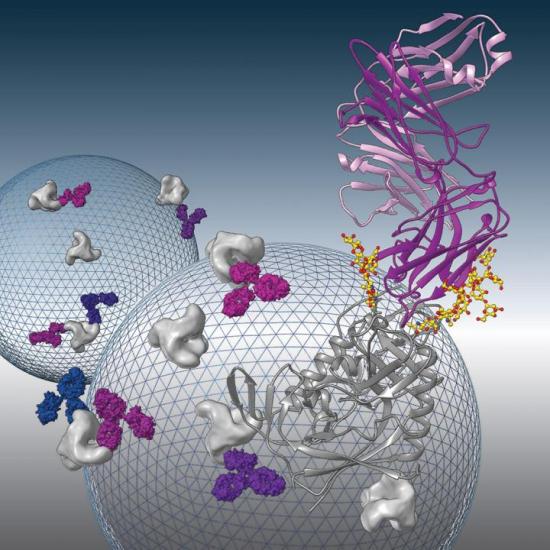
Broadly neutralizing antibodies to HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein are being evaluated as therapeutics to prevent or treat HIV-1 infection. Structural analysis of one such antibody, 8ANC195, revealed a new conformation of the envelope protein. The image shows the X-ray crystal structure of 8ANC195 in complex with the gp120 subunit of the envelope protein. The background shows schematic representations of HIV-1 virus particles studded with envelope proteins being recognized by 8ANC195 antibodies.
Image credit goes to: Louise Scharf/Caltech
Proteins called broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) are a promising key to the prevention of infection by HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. bNAbs have been found in blood samples from some HIV patients whose immune systems can naturally control the infection. These antibodies may protect a patient’s healthy cells by recognizing a protein called the envelope spike, present on the surface of all HIV strains and inhibiting, or neutralizing, the effects of the virus. Now Caltech researchers have discovered that one particular bNAb may be able to recognize this signature protein, even as it takes on different conformations during infection–making it easier to detect and neutralize the viruses in an infected patient.
Physicists show ‘molecules’ made of light may be possible
It’s not lightsaber time… at least not yet. But a team including theoretical physicists from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has taken another step toward building objects out of photons, and the findings* hint that weightless particles of light can be joined into a sort of “molecule” with its own peculiar force.
Cells from human umbilical cord blood improve cognition in Alzheimer’s disease model mice
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), which affects an estimated 26 million people worldwide, is the fourth leading cause of death among the elderly and the leading cause of dementia. Predictions are that the number of AD cases will quadruple by 2050. Although pharmacological methods for treating AD have been discovered, none significantly delay the progression of the disease.
Artificial ‘plants’ could fuel the future
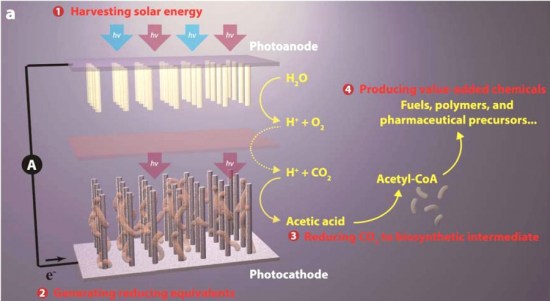
This schematic image of Chang’s artificial photosynthesis systems shows its four general components: (1) harvesting solar energy, (2) generating reducing equivalents, (3) reducing CO2 to biosynthetic intermediates and (4) producing value-added chemicals.
Image credit goes to: Berkeley Lab
Imagine creating artificial plants that make gasoline and natural gas using only sunlight. And imagine using those fuels to heat our homes or run our cars without adding any greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. By combining nanoscience and biology, researchers led by scientists at University of California, Berkeley, have taken a big step in that direction.
Tree of life study unveils inner workings of a cell
Scientists have uncovered tens of thousands of new protein interactions, accounting for about a quarter of all estimated protein contacts in a cell.
Image credit goes to: Jovana Drinkjakovic
A multinational team of scientists have sifted through cells of vastly different organisms, from amoebae to worms to mice to humans, to reveal how proteins fit together to build different cells and bodies. This tour de force of protein science, a result of a collaboration between seven research groups from three countries, led by Professor Andrew Emili from the University of Toronto’s Donnelly Centre, uncovered tens of thousands of new protein interactions, accounting for about a quarter of all estimated protein contacts in a cell.
Guilting teens into exercise won’t increase activity
Just like attempts at influencing hairstyles or clothing can backfire, adults who try to guilt middle-schoolers into exercising won’t get them to be any more active. The study found students who don’t feel in control of their exercise choices or who feel pressured by adults to be more active typically aren’t.
The science of stereotyping: Challenging the validity of ‘gaydar’
“Gaydar” — the purported ability to infer whether people are gay or straight based on their appearance — seemed to get a scientific boost from a 2008 study that concluded people could accurately guess someone’s sexual orientation based on photographs of their faces. In a new paper researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison challenge what they call “the gaydar myth.” William Cox, an assistant scientist in the Department of Psychology and the lead author, says gaydar isn’t accurate and is actually a harmful form of stereotyping.
Do antipsychotic medications affect cortical thinning?
People diagnosed with schizophrenia critically rely upon treatment with antipsychotic medications to manage their symptoms and help them function at home and in the workplace. But despite their benefits, antipsychotic medications might also have some negative effects on brain structure or function when taken for long periods of time.
Feeling blue and seeing blue: Sadness may impair color perception
The world might seem a little grayer than usual when we’re down in the dumps and we often talk about “feeling blue” — new research suggests that the associations we make between emotion and color go beyond mere metaphor. The results of two studies indicate that feeling sadness may actually change how we perceive color. Specifically, researchers found that participants who were induced to feel sad were less accurate in identifying colors on the blue-yellow axis than those who were led to feel amused or emotionally neutral.
Researchers help identify neural basis of multitasking
What makes someone better at switching between different tasks? Looking for the mechanisms behind cognitive flexibility, researchers have used brain scans to shed new light on this question. By studying networks of activity in the brain’s frontal cortex, a region associated with control over thoughts and actions, the researchers have shown that the degree to which these networks reconfigure themselves while switching from task to task predicts people’s cognitive flexibility.
The alien within: Fetal cells influence maternal health during pregnancy (and long after)
Parents go to great lengths to ensure the health and well-being of their developing offspring. The favor, however, may not always be returned. Dramatic research has shown that during pregnancy, cells of the fetus often migrate through the placenta, taking up residence in many areas of the mother’s body, where their influence may benefit or undermine maternal health.
Confidence in parenting could help break cycle of abuse
To understand how confidence in parenting may predict parenting behaviors in women who were abused as children, psychologists have found that mothers who experienced more types of maltreatment as children are more critical of their ability to parent successfully. Intervention programs for moms at-risk, therefore, should focus on bolstering mothers’ self-confidence–not just teach parenting skills, the researchers said.
HIV particles do not cause AIDS, our own immune cells do
Researchers have revealed that HIV does not cause AIDS by the virus’s direct effect on the host’s immune cells, but rather through the cells’ lethal influence on one another. HIV can either be spread through free-floating virus that directly infect the host immune cells or an infected cell can pass the virus to an uninfected cell.
Fertilization discovery: Do sperm wield tiny harpoons?
Could the sperm harpoon the egg to facilitate fertilization? That’s the intriguing possibility raised by the University of Virginia School of Medicine’s discovery that a protein within the head of the sperm forms spiky filaments, suggesting that these tiny filaments may lash together the sperm and its target.
Predicting who will murder his wife or his family
Murderers who kill intimate partners and family members have a significantly different psychological and forensic profile from murderers who kill people they don’t know, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study that examined the demographics, psychiatric history and neuropsychology of these individuals.
Want a better relationship and a better sex life?
If men take up more of the child-care duties, splitting them equally with their female partners, heterosexual couples have more satisfaction with their relationships and their sex lives, according to new research by sociologists. The group used data from more than 900 heterosexual couples’ responses in the 2006 Marital Relationship Study (MARS).
Don’t touch that dial: TV’s subliminal influence on women’s perception of pregnancy and birth
In an era where popular culture is increasingly recognized for its impact on lay understanding of health and medicine, few scholars have looked at television’s powerful role in the creation of patient expectations, especially regarding pregnancy and birth.
How long have primates been infected with viruses related to HIV?
Disease-causing viruses engage their hosts in ongoing arms races: positive selection for antiviral genes increases host fitness and survival, and viruses in turn select for mutations that counteract the antiviral host factors. Studying such adaptive mutations can provide insights into the distant history of host-virus interactions. A study of antiviral gene sequences in African monkeys suggests that lentiviruses closely related to HIV have infected primates in Africa as far back as 16 million years.
‘Memory region’ of the brain also involved in conflict resolution
The hippocampus in the brain’s temporal lobe is responsible for more than just long-term memory. Researchers have for the first time demonstrated that it is also involved in quick and successful conflict resolution.
Happiness spreads, but depression isn’t contagious
Having friends who suffer from depression doesn’t affect the mental health of others, according to research. The team found that having friends can help teenagers recover from depression or even avoid becoming depressed in the first instance. The findings are the result of a study of the way teenagers in a group of US high schools influenced each others’ mood. The academics used a mathematical model to establish if depression spreads from friend to friend.
Don’t I know that guy? Neuroscientists pinpoint part of the brain that deciphers memory from new experience


Research assistant Jeremy Johnson feeds a rat on the behavioral track used to determine where the brain decides what is new and what is familiar.
Image credit goes to: Johns Hopkins University
You see a man at the grocery store. Is that the fellow you went to college with or just a guy who looks like him? One tiny spot in the brain has the answer. Neuroscientists have identified the part of the hippocampus that creates and processes this type of memory, furthering our understanding of how the mind works, and what’s going wrong when it doesn’t.
Nicotine changes marijuana’s effect on the brain
How scientists study the effects of marijuana on the brain is changing. Until recently marijuana research largely excluded tobacco users from its participant pool, but scientists have found reason to abandon this practice, uncovering significant differences in the brains of individuals who use both tobacco and marijuana and the brains of those who only use marijuana.
How influential are peer reactions to posts on Facebook news channels?
An experiment to determine the effects of positive and negative user comments to items posted by media organizations on Facebook news channels showed, surprisingly, that the influence of user comments varied depending on the type and number of user comments. Negative comments influenced the persuasiveness of a news article, while positive comments did not, and a high number of likes did not have the expected bandwagon effect.
The stomach is the way to a woman’s heart, too
You’ve heard that romance starts in the kitchen and not in the bedroom. Well, researchers at Drexel University finally have the science to support that saying – but not the way you might think. Researchers found that women’s brains respond more to romantic cues on a full stomach than an empty one. The study explored brain circuitry in hungry versus satiated states among women who were past-dieters and those who had never dieted.
On Wikipedia, politically controversial science topics vulnerable to information sabotage
Wikipedia reigns. It’s the world’s most popular online encyclopedia, the sixth most visited website in America, and a research source most U.S. students rely on. But Wikipedia entries on politically controversial scientific topics can be unreliable due to information sabotage.
Can your brain control how it loses control?
A new study may have unlocked understanding of a mysterious part of the brain — with implications for neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s. The results open up new areas of research in the pursuit of neuroprotective therapies.
Scientists discover what controls waking up and going to sleep
Fifteen years ago, an odd mutant fruit fly caught the attention and curiosity of Dr. Ravi Allada, a circadian rhythms expert at Northwestern University, leading the neuroscientist to recently discover how an animal’s biological clock wakes it up in the morning and puts it to sleep at night. The clock’s mechanism, it turns out, is much like a light switch.
Cognitive decision making as the collapse of a quantum superstate
Decision making in an enormous range of tasks involves the accumulation of evidence in support of different hypotheses. One of the enduring models of evidence accumulation is the Markov random walk (MRW) theory, which assigns a probability to each hypothesis. In an MRW model of decision making, when deciding between two hypotheses, the cumulative evidence for and against each hypothesis reaches different levels at different times, moving particle-like from state to state and only occupying a single definite evidence level at any given point.
Study details ‘rotten egg’ gas’ role in autoimmune disease
The immune system not only responds to infections and other potentially problematic abnormalities in the body, it also contains a built-in brake in the form of regulatory T cells, or Tregs. Tregs ensure that inflammatory responses don’t get out of hand and do damage. In autoimmune diseases, sometimes these Treg cells don’t act as they should.
Research advances potential for test and vaccine for genital and oral herpes
Findings from a pair of new studies could speed up the development of a universally accurate diagnostic test for human herpes simplex viruses (HSV), according to researchers at Johns Hopkins and Harvard universities and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The work may also lead to the development of a vaccine that protects against the virus.
Researchers resurrect ancient viruses in hopes of improving gene therapy
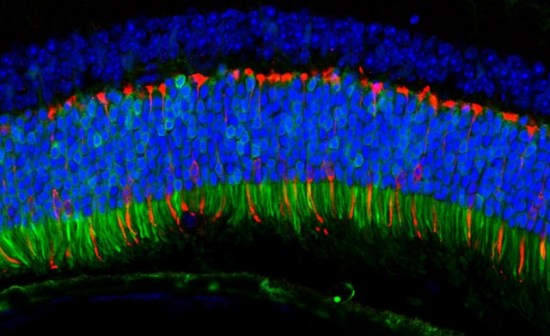
The Anc80 virus delivered genes to the mouse retina that fluoresce green when expressed. Pictured here, the delivered genes are active in the retina’s color-detecting cells.
Image credit goes to: Livia Carvalho
It sounds like the start of a horror movie, but Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI) researchers at Massachusetts Eye and Ear (MEE) have reconstructed an ancient virus that is highly effective at delivering gene therapies to the liver, muscle, and retina. This discovery could potentially be used to design gene therapies that are not only safer and more potent than therapies currently available, but may also help a greater number of patients.
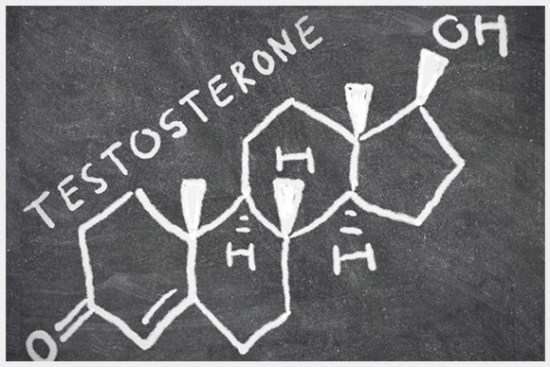
Study of 83,000 veterans finds cardiovascular benefits to testosterone replacement
A Veterans Affairs database study of more than 83,000 patients found that men whose low testosterone was restored to normal through gels, patches, or injections had a lower risk of heart attack, stroke, or death from any cause, versus similar men who were not treated. The study also found that men who were treated but did not attain normal levels did not see the same benefits as those whose levels did reach normal.
Music and the mind: Can music help people with epilepsy?
The brains of people with epilepsy appear to react to music differently from the brains of those who do not have the disorder, a finding that could lead to new therapies to prevent seizures, according to research.
Good for the relationship: A reframing of sexting
The practice of sexting may be more common than generally thought among adults. More than eight out of 10 people surveyed online admitted to sexting in the prior year, according to new research.