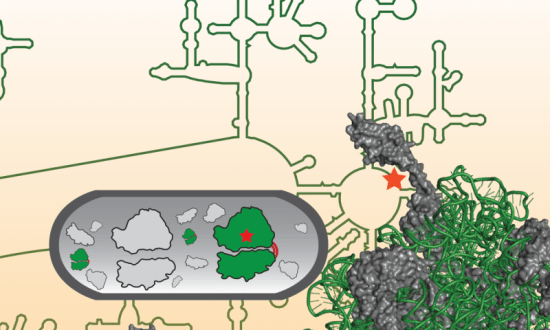
Decision making in an enormous range of tasks involves the accumulation of evidence in support of different hypotheses. One of the enduring models of evidence accumulation is the Markov random walk (MRW) theory, which assigns a probability to each hypothesis. In an MRW model of decision making, when deciding between two hypotheses, the cumulative evidence for and against each hypothesis reaches different levels at different times, moving particle-like from state to state and only occupying a single definite evidence level at any given point.
Latest
Study details ‘rotten egg’ gas’ role in autoimmune disease
The immune system not only responds to infections and other potentially problematic abnormalities in the body, it also contains a built-in brake in the form of regulatory T cells, or Tregs. Tregs ensure that inflammatory responses don’t get out of hand and do damage. In autoimmune diseases, sometimes these Treg cells don’t act as they should.
Research advances potential for test and vaccine for genital and oral herpes
Findings from a pair of new studies could speed up the development of a universally accurate diagnostic test for human herpes simplex viruses (HSV), according to researchers at Johns Hopkins and Harvard universities and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The work may also lead to the development of a vaccine that protects against the virus.
Researchers resurrect ancient viruses in hopes of improving gene therapy
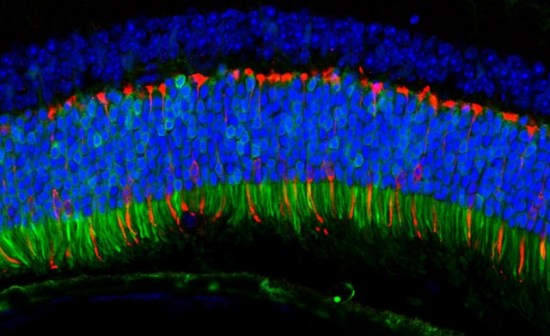
The Anc80 virus delivered genes to the mouse retina that fluoresce green when expressed. Pictured here, the delivered genes are active in the retina’s color-detecting cells.
Image credit goes to: Livia Carvalho
It sounds like the start of a horror movie, but Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI) researchers at Massachusetts Eye and Ear (MEE) have reconstructed an ancient virus that is highly effective at delivering gene therapies to the liver, muscle, and retina. This discovery could potentially be used to design gene therapies that are not only safer and more potent than therapies currently available, but may also help a greater number of patients.
Study of 83,000 veterans finds cardiovascular benefits to testosterone replacement
A Veterans Affairs database study of more than 83,000 patients found that men whose low testosterone was restored to normal through gels, patches, or injections had a lower risk of heart attack, stroke, or death from any cause, versus similar men who were not treated. The study also found that men who were treated but did not attain normal levels did not see the same benefits as those whose levels did reach normal.
Music and the mind: Can music help people with epilepsy?
The brains of people with epilepsy appear to react to music differently from the brains of those who do not have the disorder, a finding that could lead to new therapies to prevent seizures, according to research.
Good for the relationship: A reframing of sexting
The practice of sexting may be more common than generally thought among adults. More than eight out of 10 people surveyed online admitted to sexting in the prior year, according to new research.
Switching mouse neural stem cells to a primate-like behavior
When the right gene is expressed in the right manner in the right population of stem cells, the developing mouse brain can exhibit primate-like features. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) succeeded in mimicking the sustained expression of the transcription factor Pax6 as seen in the developing human brain, in mouse cortical progenitor cells. This altered the behavior of these cells to one that is akin to that of progenitors in the developing primate neocortex. Consequently, the mouse progenitors generated more neurons – a prerequisite for a bigger brain.
Excessive workout supplement use: An emerging eating disorder in men?
In an effort to build better bodies, more men are turning not to illegal anabolic steroids, but to legal over-the-counter bodybuilding supplements to the point where it may qualify as an emerging eating disorder, according to research presented at the American Psychological Association’s annual convention.
Cellular zombies: Mutant cells that can’t copy DNA keep dividing when they shouldn’t

Sequential images of abnormal divisions in a mutant cell leading to abnormal nuclei and chromosome rearrangement. Chromosomes are displayed in pink, cell membranes in green. The cell undergoes two aberrant divisions.
Image credit goes to: Susan Forsburg
Researchers at USC have developed a yeast model to study a gene mutation that disrupts the duplication of DNA, causing massive damage to a cell’s chromosomes, while somehow allowing the cell to continue dividing.
How to tell the difference between bipolar disorder and depression
Many patients with bipolar disorder, a debilitating mental condition that can take a person from the sluggishness of severe depression to super-human energy levels, are often misdiagnosed as having major depressive disorder, or MDD. But now as an alternative to reliance on patient interviews, scientists are closing in on an objective test that could help clinicians distinguish between the two — and provide better treatment.
Mans best friend: Dogs process faces in specialized brain area
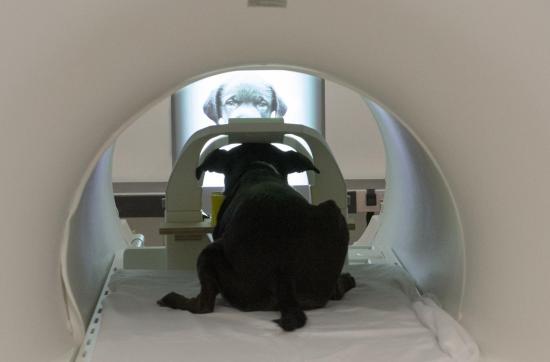
The study involved dogs viewing both static images and video images on a screen while undergoing fMRI. It was a particularly challenging experiment since dogs do not normally interact with two-dimensional images, and they had to undergo training to learn to pay attention to the screen.
Image credit goes to: Photo by Gregory Berns, Emory University
Ever feel like your pet knows what you look like? While historically animals are depicted as, well slow… new research is proving otherwise. To pet owners this might not be big news, but scientists found that dogs have a specialized region in their brains for processing faces. The research provides the first evidence for a face-selective region in the temporal cortex of dogs.
Preventing addiction relapse by erasing drug-associated memories
Recovering addicts often grapple with the ghosts of their addiction–memories that tempt them to relapse even after rehabilitation and months, or even years, of drug-free living. Now, scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have made a discovery that brings them closer to a new therapy based on selectively erasing these dangerous and tenacious drug-associated memories.
Stem cells: From pluripotency to totipotency
While it is already possible to obtain in vitro pluripotent cells (ie, cells capable of generating all tissues of an embryo) from any cell type, researchers from Maria-Elena Torres-Padilla’s team have pushed the limits of science even further. They managed to obtain totipotent cells with the same characteristics as those of the earliest embryonic stages and with even more interesting properties. Read the rest of this page »
New approach for making vaccines for deadly diseases
Researchers have devised an entirely new approach to vaccines – creating immunity without vaccination. The team has demonstrated that animals injected with synthetic DNA engineered to encode a specific neutralizing antibody against the dengue virus were capable of producing the exact antibodies necessary to protect against disease, without the need for standard antigen-based vaccination. Importantly, this approach, termed DMAb, was rapid, protecting animals within a week of administration.
Childhood cancer cells drain immune system’s batteries
Cancer cells in neuroblastoma contain a molecule that breaks down a key energy source for the body’s immune cells, leaving them too physically drained to fight the disease, according to new research. Cancer Research UK-funded scientists have discovered that the cells in neuroblastoma – a rare type of childhood cancer that affects nerve cells – produce a molecule that breaks down arginine, one of the building blocks of proteins and an essential energy source for immune cells.
Crystal clear images uncover secrets of hormone receptors
Many hormones and neurotransmitters work by binding to receptors on a cell’s exterior surface. This activates receptors causing them to twist, turn and spark chemical reactions inside cells. NIH scientists used atomic level images to show how the neuropeptide hormone neurotensin might activate its receptors. Their description is the first of its kind for a neuropeptide-binding G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), a class of receptors involved in a wide range of disorders and the target of many drugs.
Paralyzed men move legs with new non-invasive spinal cord stimulation
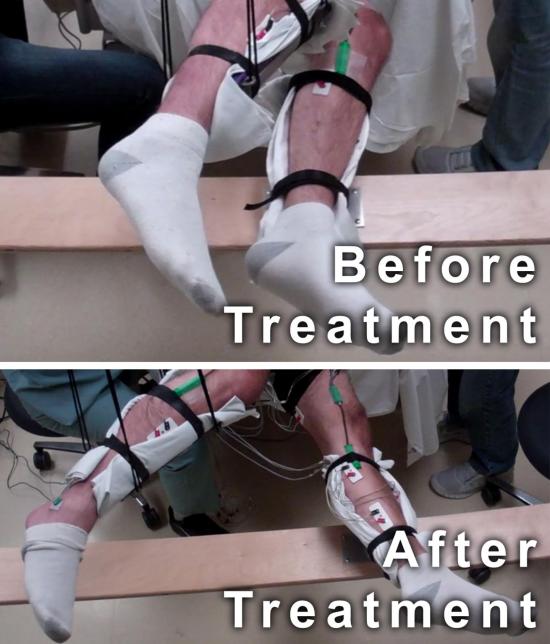
This image shows the range of voluntary movement prior to receiving stimulation compared to movement after receiving stimulation, physical conditioning, and buspirone. The subject’s legs are supported so that they can move without resistance from gravity. The electrodes on the legs are used for recording muscle activity.
Image credit goes to: Edgerton lab/UCLA
Five men with complete motor paralysis were able to voluntarily generate step-like movements thanks to a new strategy that non-invasively delivers electrical stimulation to their spinal cords. The strategy, called transcutaneous stimulation, delivers electrical current to the spinal cord by way of electrodes strategically placed on the skin of the lower back.
We can build it better: The first artificial ribosome
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago and Northwestern University have engineered a tethered ribosome that works nearly as well as the authentic cellular component, or organelle, that produces all the proteins and enzymes within the cell. The engineered ribosome may enable the production of new drugs and next-generation biomaterials and lead to a better understanding of how ribosomes function.
Prostate cancer is 5 different diseases
Cancer Research UK scientists have for the first time identified that there are five distinct types of prostate cancer and found a way to distinguish between them, according to a landmark study. The findings could have important implications for how doctors treat prostate cancer in the future, by identifying tumours that are more likely to grow and spread aggressively through the body.
Where memory is encoded and retrieved
Are the same regions and even the same cells of the brain area called hippocampus involved in encoding and retrieving memories or are different areas of this structure engaged? This question has kept neuroscientists busy for a long time. Researchers at the Mercator Research Group “Structure of Memory” at RUB have now found out that the same brain cells exhibit activity in both processes.
Some vaccines support evolution of more-virulent viruses

This image shows chickens in agricultural production. Image credit goes to: Andrew Read, Penn State University
Scientific experiments with the herpes virus such as the one that causes Marek’s disease in poultry have confirmed, for the first time, the highly controversial theory that some vaccines could allow more-virulent versions of a virus to survive, putting unvaccinated individuals at greater risk of severe illness. The research has important implications for food-chain security and food-chain economics, as well as for other diseases that affect humans and agricultural animals.
Sleep not just protects memories against forgetting, it also makes them more accessible
Sleeping not only protects memories from being forgotten, it also makes them easier to access, according to new research from the University of Exeter and the Basque Centre for Cognition, Brain and Language. The findings suggest that after sleep we are more likely to recall facts which we could not remember while still awake.
Cell phone notifications may be driving you to distraction
Whether you are alerted to an incoming phone call or text by a trendy ringtone, an alarm bell or a quiet vibration, just receiving a notification on your cell phone can cause enough of a distraction to impair your ability to focus on a given task. In fact, the distraction caused by a simple notification — whether it is a sound or a vibration — is comparable to the effects seen when users actively use their cell phones to make calls or send text messages, the researchers found.
Spines of boys and girls differ at birth
Looking at measurements of the vertebrae – the series of small bones that make up the spinal column – in newborn children, investigators at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles found that differences between the sexes are present at birth. Results of the study suggest that this difference is evolutionary, allowing the female spine to adapt to the fetal load during pregnancy.
Brain structure reveals ability to regulate emotions
We all vary in how often we become happy, sad or angry, and also in how strongly these emotions are expressed. This variability is a part of our personality and can be seen as a positive aspect that increases diversity in society. However, there are people that find it so difficult to regulate their emotions that it has a serious impact on their work, family and social life. These individuals may be given an emotional instability diagnosis such as borderline personality disorder or antisocial personality disorder.
Using low-dose irradiation, researchers can now edit human genes
For the first time, researchers have employed a gene-editing technique involving low-dose irradiation to repair patient cells. This method, developed by researchers in the Cedars-Sinai Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute, is 10 times more effective than techniques currently in use.
Static synapses on a moving structure: Mind the gap!
In biology, stability is important. From body temperature to blood pressure and sugar levels, our body ensures that these remain within reasonable limits and do not reach potentially damaging extremes. Neurons in the brain are no different and, in fact, have developed a number of ways to stabilise their electrical activity so as to avoid becoming either overexcitable, potentially leading to epilepsy, or not excitable enough, leading to non functional neurons.
Drawing a line between quantum and classical world
Quantum theory is one of the great achievements of 20th century science, yet physicists have struggled to find a clear boundary between our everyday world and what Albert Einstein called the “spooky” features of the quantum world, including cats that could be both alive and dead, and photons that can communicate with each other across space instantaneously.
Research investigates whether solar events could trigger birth defects on Earth
Studies find airplane crews at high altitude are exposed to potentially harmful levels of radiation from cosmic rays. But could these cosmic rays pose hazards even at sea level? In recent years, research has suggested congenital birth defects down on Earth’s surface could be caused by these “solar particle events” — spikes in cosmic rays from the sun that touch off the northern lights and sometimes hamper communications or the electric power grid.
Dead galaxies in Coma Cluster may be packed with dark matter

This artist’s impression of the ‘quenching’ process shows how a normal blue (star-forming) galaxy lost its gas while falling into the Coma Cluster very early on in its formation.
Image credit goes to: Ameron Yozin, ICRAR/UWA
Galaxies in a cluster roughly 300 million light years from Earth could contain as much as 100 times more dark matter than visible matter, according to an Australian study. The research, published today, used powerful computer simulations to study galaxies that have fallen into the Coma Cluster, one of the largest structures in the Universe in which thousands of galaxies are bound together by gravity.
Study finds metal foams capable of shielding X-rays, gamma rays, neutron radiation

Research from North Carolina State University shows that lightweight composite metal foams — like the one pictured here — are effective at blocking X-rays, gamma rays and neutron radiation, and are capable of absorbing the energy of high impact collisions. The finding means the metal foams hold promise for use in nuclear safety, space exploration and medical technology applications.
Image credit goes to: Afsaneh Rabiei, North Carolina State University
Research from North Carolina State University shows that lightweight composite metal foams are effective at blocking X-rays, gamma rays and neutron radiation, and are capable of absorbing the energy of high impact collisions. The finding means the metal foams hold promise for use in nuclear safety, space exploration and medical technology applications.
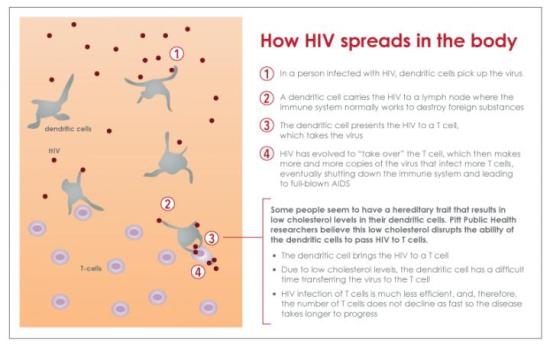
Cholesterol metabolism in immune cells linked to HIV progression, may lead to new therapy
Enhanced cholesterol metabolism in certain immune cells may help some people infected with HIV naturally control disease progression, according to new research. The findings provide a basis for potential development of new approaches to control HIV infection by regulating cellular cholesterol metabolism.
Women and fragrances: Scents and sensitivity
Researchers have sniffed out an unspoken rule among women when it comes to fragrances: Women don’t buy perfume for other women, and they certainly don’t share them. Like boyfriends, current fragrance choices are hands off, forbidden–neither touch, nor smell. You can look, but that’s all, says BYU industrial design professor and study coauthor Bryan Howell.
What’s that!? Brain network that controls, redirects attention identified
Researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) have found that key parts of the human brain network that give us the power to control and redirect our attention–a core cognitive ability–may be unique to humans. The research suggests that the network may have evolved in response to increasingly complex social cues.
Vaginal douches may expose women to harmful phthalate chemicals
Women who use feminine care products called douches may increase their exposure to harmful chemicals called phthalates–and black women may be at particularly high risk due to frequent use. Public health officials advise against the use of douching products, which can hide vaginal infections and lead to other serious health problems. Despite that, douching products are still a popular item on the drug store shelf, and are disproportionately used by black women.
Intellectual pursuits may buffer the brain against addiction
New study of mice finds that intellectual pursuits can make us more resistant to the lure of drugs Image credit goes to: Emily Strange)
Challenging the idea that addiction is hardwired in the brain, a new study suggests that even a short time spent in a stimulating learning environment can rewire the brain’s reward system and buffer it against drug dependence. Scientists tracked cocaine cravings in more than 70 adult male mice and found that those rodents whose daily drill included exploration, learning and finding hidden tasty morsels were less likely than their enrichment-deprived counterparts to seek solace in a chamber where they had been given cocaine.
Baby’s first stool can alert doctors to future cognitive issues
A newborn’s first stool can signal the child may struggle with persistent cognitive problems, according to Case Western Reserve University Project Newborn researchers. In particular, high levels of fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEE) found in the meconium (a newborn’s first stool) from a mother’s alcohol use during pregnancy can alert doctors that a child is at risk for problems with intelligence and reasoning.
Less intensive chemo avoids irreversible side effects in children’s cancer
Children with a rare type of cancer called Wilms’ tumour who are at low risk of relapsing can now be given less intensive treatment, avoiding a type of chemotherapy that can cause irreversible heart problems in later life. The move follows the results of a Cancer Research UK trial showing that the drug doxorubicin can be safely omitted from treatment without affecting patients’ chances of survival.
Spinal cord injury and the bodies response: Modulating the macrophage
Macrophages are cellular sentinels in the body, assigned to identify “attacks” from viruses, bacteria, or fungi and sound the alarm when they are present. However, these cells are a “double edged sword” in spinal cord injury, providing both neural repair-promoting properties and pathological functions that destroy neuronal tissue.
A new wrinkle: Geometry of brain’s outer surface correlates with genetic heritage
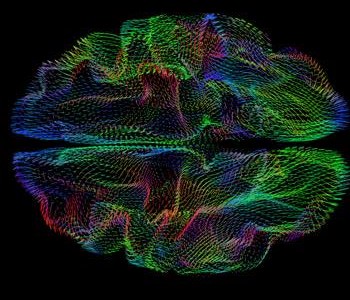
In the study, the researchers found that the shape of the cerebral cortex correlates with genetic ancestry. Image credit goes to: UC San Diego
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego and the School of Medicine have found that the three-dimensional shape of the cerebral cortex – the wrinkled outer layer of the brain controlling many functions of thinking and sensation – strongly correlates with ancestral background. The study opens the door to more precise studies of brain anatomy going forward and could eventually lead to more personalized medicine approaches for diagnosing and treating brain diseases.
Study finds violent video games provide quick stress relief, but at a price
A study authored by two University of Wisconsin-Madison graduate students indicates that while playing video games can improve mood, violent games may increase aggressive outcomes. The researchers looked at how video games may be used to manage emotions — specifically, whether playing the games can improve mood.
Study shows long-term effects of type 2 diabetes on the brain, thinking
In just two years, people with type 2 diabetes experienced negative changes in their ability to regulate blood flow in the brain, which was associated with lower scores on tests of cognition skills and their ability to perform their daily activities, according to a new study.
How the tumor escapes the immune response
Natural killer cells of the immune system can fend off malignant lymphoma cells and thus are considered a promising therapeutic approach. However, in the direct vicinity of the tumor they lose their effect. Scientists have now elucidated which mechanisms block the natural killer cells and how this blockade could be lifted.
Pupil response predicts depression risk in kids

Findings suggest that physiological reactivity to sad stimuli, assessed using pupillometry, serves as one potential biomarker of depression risk among children of depressed mothers. Image credit goes to: Jonathan Cohen, Binghamton University Photographer
Most parents don’t want to think about their children as depressed, but that can be a deadly mistake. Short of clinical diagnosis through cost prohibitive therapy, there is no real way to tell if a child is at risk for depression. However, according to new research from Binghamton University , how much a child’s pupil dilates in response to seeing an emotional image can predict his or her risk of depression over the next two years.